Public Key
Child public keys can be derived from both private and public keys. The child can be hardened if the parent is private. Attempting to create a hardened child using a public key will result in an error. Non-hardened keys are still useful, but need to be handled carefully to avoid security risks. For more information about the concept of a hardened child read BIP-32.
Deriving a Child Public Key
Derive HD Wallet Private Key uses an extended private key to create a child key with specified parameters.
This function requires inputs as follows:
- Key 1 : The key used in the derivation process. Invalid and public (if the child is hardened) keys will cause the operation to fail.
- Child Type 2 : Type of child to create. This allows for the child key to be hardened if needed.
- Child Index 3 : The number of the child. It is an index between 0 and 231-1. Hardened child keys will have their index shifted by 231 when serialized to match BIP-32 specification.
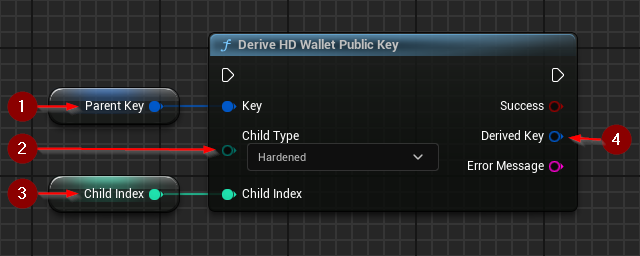
If the operation is successful, the value Derived Key 4 will hold the generated valid child public key.